
#Create a stem plot series
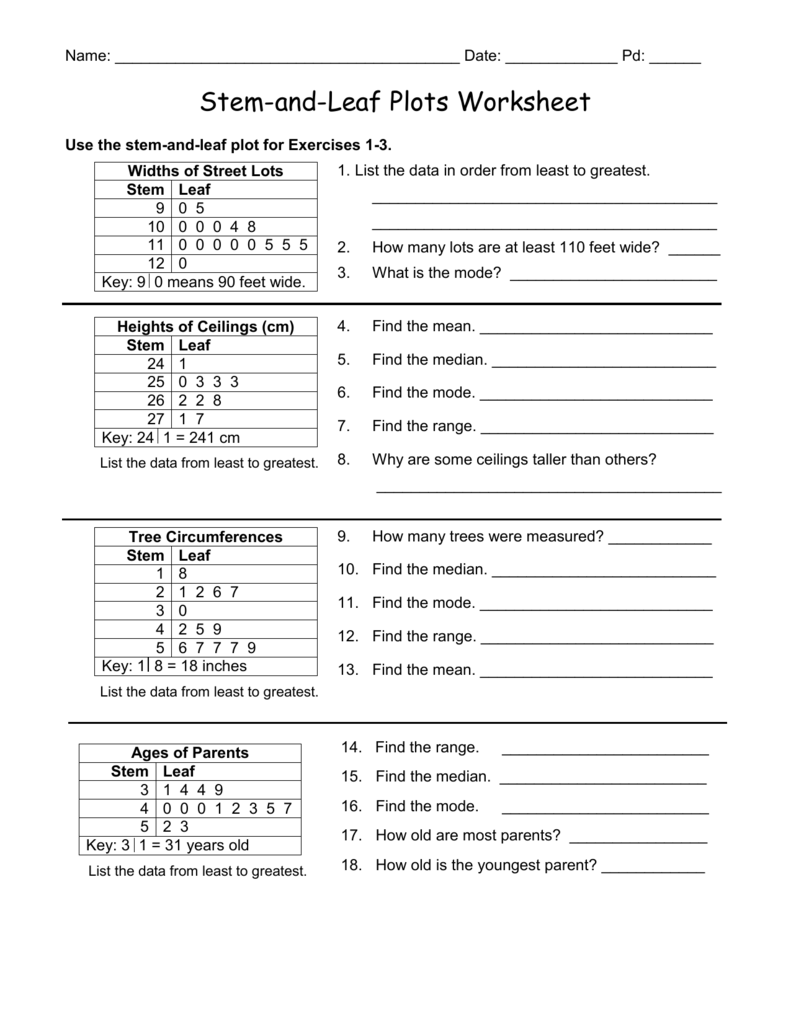
Stem and Leaf plots are very useful because they allow us to see the distributions across different categories of data without the use of complex mathematical computations.Ī stem and leaf plot displays a series of scores in a simple and comprehensible way. It is usually numbered 0-9 depending on the range of the dataset you are working with.
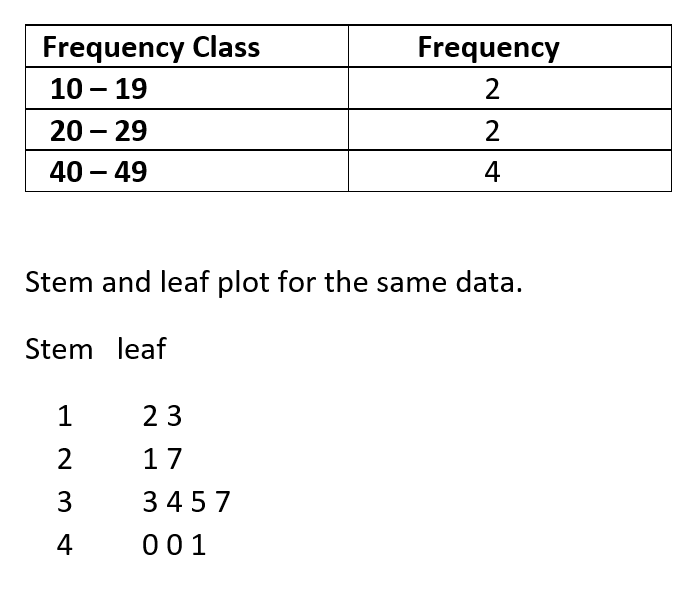
Leaf: The leaf represents the number farthest to the right.
Count: This represents the number of data points with that first digit.Stems: This represents the first digit or digits of the data points.The individual character in a stem and leaf plot is described as follows: The numbers are usually broken into smaller pieces per row, for example, it can be broken into 10s or 100s. It depends on the preference of the individual plotting the stem and leaf plot. These numbers may or may not be sorted in an ascending order or descending order. In addition, if you set the argument back.to.back as FALSE, the plots won’t be displayed back-to-back: (data, data2, back.to.A Stem and Leaf Plot can easily be described as a table or chart that visualizes the distribution of numbers within a specified range. Other interesting function of the aplpack package is that allows you to compare two stem and leaf plots with the function, that by default plots a back-to-back (two sided) stem and leaf display: # install.packages("aplpack") stem(data, scale = 3) The decimal point is 1 digit(s) to the right of the |Ĭomparative (back to back) stem and leaf diagram in R In this example, the first of the duplicated stem shows the leafs corresponding to values lower than 5 and the second the leafs corresponding to values equal or higher to 5. Note that if you set scale = 3, each stem will be duplicated. In order to solve this issue you can change the height of the plot with the scale argument as follows: stem(data, scale = 2) The decimal point is 1 digit(s) to the right of the |

This is due to the stems are grouped (the first stem is for 0 and 1, the second for 2 and 3, and so on). However, you may have noticed that the output is not equal to the example we reviewed in the first section. Note that, to clarify, in the comments we show the corresponding values to each stem. The output is the text displayed in the following block. You can create a simple stem plot typing: stem(data) It should be noted that if the input argument contains non-finite or missing values they are not taken into account. The syntax of the function is as follows: stem(x, # Numeric vector The stem function allows you to create a stem and leaf plot in R.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
